Coronary Artery Bypass Graft: All You Wanted to Know
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a common heart condition that affects millions of people worldwide. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications and even death. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available, and one of the most effective ones is Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG). In this article, we will explore what CABG is, when it is recommended, how the procedure is performed, the recovery process, and more.

Understanding Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease occurs when the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients become narrow or blocked due to a buildup of plaque. This can restrict blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and other symptoms. The primary causes of CAD include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle.
What is Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)?
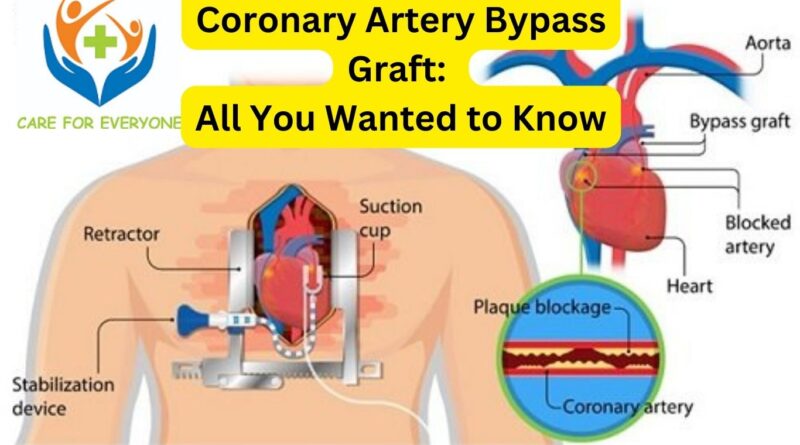
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) is a surgical procedure that aims to restore proper blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. During CABG, a healthy blood vessel, typically taken from the leg, arm, or chest, is grafted onto the blocked artery, creating an alternative pathway for blood to reach the heart. This procedure can improve blood flow, relieve symptoms, and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
There are different types of CABG procedures, including:
- Traditional CABG: Involves a large incision in the chest and the use of a heart-lung bypass machine.
- Off-pump CABG: The heart-lung bypass machine is not used, and the procedure is performed while the heart is still beating.
- Minimally invasive CABG: Involves smaller incisions and specialized instruments, resulting in faster recovery and reduced scarring.
When is CABG Recommended?
CABG is typically recommended when other treatments, such as medication or lifestyle changes, have not effectively managed the symptoms of coronary artery disease. The following indications may warrant CABG:
- Severe blockages in multiple coronary arteries
- Left main coronary artery disease
- Reduced heart function
- Failed previous interventions, such as angioplasty or stenting
- Recurrent chest pain despite optimal medical therapy
To determine if CABG is appropriate, doctors may perform various diagnostic tests, including coronary angiography, stress tests, and imaging studies.
Preparing for CABG
Before undergoing CABG, a comprehensive medical evaluation will be conducted to assess the patient’s overall health and readiness for surgery. This evaluation may involve blood tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, and other relevant assessments. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, adopting a healthy diet, and managing other medical conditions, may be recommended to optimize the outcome of the surgery.
The CABG Procedure
The CABG procedure involves several steps:
- Preoperative preparations: The patient will be prepared for surgery, which includes administering anesthesia and ensuring proper monitoring.
- Anesthesia and incision: General anesthesia is administered, and a large incision is made in the chest to access the heart.
- Grafting process: The surgeon will harvest a healthy blood vessel, usually from the leg or another location, and graft it onto the blocked coronary artery, bypassing the obstruction.
- Postoperative care: After the grafts are in place, the chest incision is closed, and the patient is moved to the intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring. Pain management, wound care, and other postoperative measures are implemented.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Following CABG, the patient will typically spend a few days in the hospital, with the exact duration depending on individual circumstances. Medications, such as blood thinners and pain relievers, will be prescribed to manage symptoms and aid in the healing process. Once discharged, the patient will be advised on lifestyle modifications, including diet and exercise, and scheduled for regular follow-up appointments.
Cardiac rehabilitation, a supervised program that combines exercise, education, and counseling, is often recommended to enhance recovery and reduce the risk of future heart problems. This program helps patients regain strength, improve cardiovascular health, and adopt healthy habits.
Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, CABG carries certain risks. These can include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Blood clots
- Stroke
- Heart rhythm disturbances
- Kidney problems
However, with advances in surgical techniques and improved postoperative care, the risks associated with CABG have significantly decreased. It is essential for patients to follow their doctor’s instructions, attend regular check-ups, and promptly report any concerning symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes after CABG
To maintain the benefits of CABG and promote long-term heart health, lifestyle changes are crucial. These may include:
- Diet and nutrition: Following a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
- Exercise and physical activity: Engaging in regular aerobic exercise and incorporating strength training, as recommended by healthcare professionals.
- Stress management: Adopting stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or counseling.
- Avoiding tobacco: Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke.
- Managing other medical conditions: Effectively managing conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol through medication and lifestyle modifications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How long does it take to recover from CABG surgery?
- The recovery period can vary, but most patients can resume normal activities within 6 to 12 weeks after surgery.
- Can CABG completely cure coronary artery disease?
- CABG can improve symptoms, reduce the risk of heart attacks, and increase lifespan, but it does not cure the underlying disease. Lifestyle changes and medications may still be necessary.
- Are there any dietary restrictions after CABG surgery?
- Following a heart-healthy diet, which includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and limited saturated fats and sodium, is recommended.
- Can CABG be performed on an emergency basis?
- CABG can be performed on an emergency basis in cases of severe heart attacks or other life-threatening situations.
- What are the alternatives to CABG?
- Alternatives to CABG include medication therapy, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and lifestyle changes. The appropriate treatment depends on individual circumstances and the severity of the disease.
Conclusion
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is a highly effective surgical procedure for treating coronary artery disease. It helps restore blood flow to the heart, relieve symptoms, and reduce the risk of heart attacks. By understanding the indications, procedure, recovery process, and necessary lifestyle changes, patients can make informed decisions and actively participate in their cardiac care. Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals and adherence to prescribed medications and lifestyle modifications are crucial for long-term heart health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is CABG a safe procedure?
- CABG is generally considered safe, with low complication rates. However, like any surgery, it carries some risks, which your healthcare team will discuss with you.
- Can CABG be performed on elderly patients?
- CABG can be performed on elderly patients, but individual health conditions and overall fitness will be assessed to determine the suitability of the procedure.
- How long does the CABG procedure take?
- The duration of the CABG procedure varies, but it typically takes around 3 to 6 hours, depending on the complexity of the case.
- Are there any restrictions on physical activity after CABG?
- Initially, there may be restrictions on strenuous activities, but gradually, patients can resume regular physical activities as advised by their healthcare team.
- What is the success rate of CABG?
- CABG has a high success rate in improving blood flow, relieving symptoms, and extending life expectancy. However, individual outcomes may vary based on various factors.