Backache Or Sciatica -Learn How To Get Rid Of Your Pain

Image Source: Canva Pro
Back pain is a common problem that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by a variety of factors, such as poor posture, injury, or aging. Sciatica, on the other hand, is a specific type of back pain that affects the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down to the legs.
While back pain and sciatica can be debilitating, there are several treatments and lifestyle changes that can help alleviate the pain and discomfort. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for back pain and sciatica, as well as some preventative measures you can take to reduce the risk of experiencing these conditions.
Backache or Sciatica – what you have?
Do you have backache? Does your back hurt every time you try to stand up after sitting or bend down? Are you suffering from back pain which is radiating or shooting to your hips or legs? Or your have sciatica?
In OPD I daily see at least one patient of lower backache with pain shooting or radiating to hips or legs. Sometimes they are suffering from this many years.
The below article will inform you what to do when you have such pan and how to treat or do it at home.
Back pain is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor posture, muscle strains, disc herniation, or degenerative changes in the spine. It can affect any part of the back, from the neck to the lower back, and can range from mild to severe.
Sciatica, on the other hand, is a specific type of back pain that is caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down to the legs. Symptoms of sciatica include pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the lower back, buttocks, or legs.
In summary, back pain is a broad term that refers to any type of pain in the back, while sciatica is a specific type of back pain caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve.
What is Back Pain?
Back pain is a common condition that can affect people of all ages and can be caused by a variety of factors. It is characterized by pain or discomfort in the back, which can range from mild to severe and can be acute or chronic in nature.
The back is made up of bones, muscles, ligaments, and nerves that work together to support the body and allow movement. Back pain can occur in any part of the back, from the neck to the lower back, and can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Muscle strains or sprains
- Poor posture
- Disc herniation or bulging discs
- Degenerative changes in the spine
- Arthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Spinal stenosis
- Scoliosis
- Infections or tumors
Symptoms of back pain can vary depending on the cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include a dull or sharp pain in the back, stiffness or limited mobility, muscle spasms, and difficulty standing or sitting for long periods of time.
Treatment for back pain will depend on the underlying cause of the condition and may include pain relief medications, physical therapy, exercises, stretching, or in severe cases, surgery.
Sciatica : The Real Deal
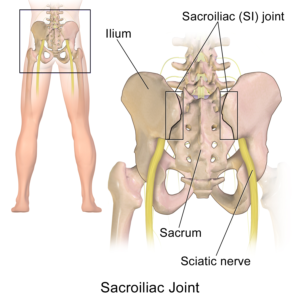
Sciatica is a condition that causes pain, numbness, and/or tingling sensations that radiate from the lower back down to the legs. It is caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, which is the largest nerve in the body and runs from the lower back down to the legs.
The most common cause of sciatica is a herniated disc, which occurs when one of the discs in the spine bulges or ruptures and puts pressure on the sciatic nerve. Other causes of sciatica include spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal), degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis (a condition where one vertebra slips out of place), and piriformis syndrome (compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle).
Symptoms of sciatica can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but they typically include:
- Pain that radiates from the lower back down to the legs, usually on one side of the body
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the legs or feet
- Weakness or difficulty moving the legs or feet
- Pain that worsens with prolonged sitting or standing
- Sharp or shooting pain when coughing, sneezing, or straining
Treatment for sciatica typically involves a combination of pain management and physical therapy. Pain management may include over-the-counter pain medications, prescription medications, or injections to help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Physical therapy may include exercises to help strengthen the muscles in the back and legs, as well as stretches to help relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve.
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve and alleviate symptoms. However, surgery is usually considered a last resort and is only recommended if other treatments have been ineffective.
Possible Causes of Back Pain and Sciatica
Back pain and sciatica can have many different causes, some of which are more common than others. Here are some possible causes of back pain and sciatica:
- Herniated or bulging discs: This occurs when the discs between the vertebrae in the spine bulge or rupture, putting pressure on nearby nerves.
- Degenerative disc disease: This occurs when the discs in the spine break down over time, causing pain and discomfort.
- Spinal stenosis: This is a narrowing of the spinal canal that can put pressure on the nerves and cause pain.
- Spondylolisthesis: This is a condition where one vertebra slips out of place and onto the vertebra below it, causing pressure on the nerves.
- Osteoarthritis: This is a type of arthritis that affects the joints in the spine and can cause pain and stiffness.
- Piriformis syndrome: This occurs when the piriformis muscle in the buttocks presses on the sciatic nerve, causing pain and discomfort.
- Trauma or injury: This can include fractures, sprains, or strains to the back or spine.
- Poor posture: Sitting or standing with poor posture can cause strain on the muscles and ligaments in the back, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Obesity: Carrying excess weight can put added strain on the back and spine, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Other medical conditions: Conditions such as scoliosis, fibromyalgia, and spinal tumors can also cause back pain and sciatica.
What is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, is a common condition that can cause back pain and sciatica. The spine is made up of small bones called vertebrae, which are separated by soft, rubbery discs that act as shock absorbers. These discs have a tough outer layer and a soft, gel-like center.
A herniated disc occurs when the tough outer layer of the disc tears, allowing the soft center to bulge or leak out. This can put pressure on the nearby nerves in the spine, causing pain, numbness, and weakness in the back and legs.
Herniated discs are most common in the lower back (lumbar spine) and the neck (cervical spine). The most common cause of a herniated disc is age-related wear and tear on the spine, but it can also be caused by trauma, injury, or improper lifting techniques.
Symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location and severity of the herniation. Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the back or neck
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the arms, legs, or feet
- Weakness or difficulty moving the arms, legs, or feet
- Pain that worsens with movement, coughing, or sneezing
- Loss of bladder or bowel control (in severe cases)
Treatment for a herniated disc usually involves a combination of pain management and physical therapy. Pain management may include over-the-counter pain medications, prescription medications, or injections to help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Physical therapy may include exercises to help strengthen the muscles in the back and improve flexibility. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerves and alleviate symptoms.
This is how a bulged disc looks like –
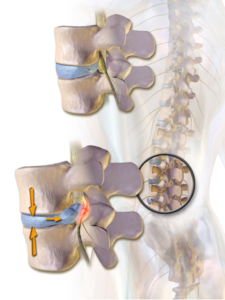
Symptoms of Back Pain and Sciatica
The symptoms of back pain and sciatica can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common symptoms:
- Back pain: This can be a dull, achy pain or a sharp, stabbing pain that can be felt anywhere in the back.
- Radiating pain: Pain that radiates from the lower back down to the legs is a common symptom of sciatica.
- Numbness or tingling sensations: This can be felt in the legs, feet, or toes.
- Weakness: Weakness in the legs or feet can occur due to pressure on the nerves.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control: In rare cases, sciatica can cause loss of bladder or bowel control, which requires immediate medical attention.
- Pain with movement: Pain can worsen with movement, such as bending, lifting, or standing for long periods of time.
- Muscle spasms: This can occur in the back or legs and can be very painful.
- Difficulty walking: This can occur due to weakness, pain, or numbness in the legs.
- Shooting pain: This can occur when coughing, sneezing, or straining.
- Difficulty sitting or standing: Pain can worsen when sitting or standing for prolonged periods.
It’s important to note that not all back pain or leg pain is caused by sciatica. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
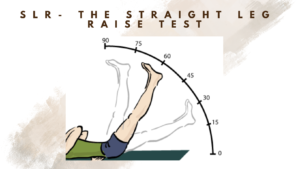
The straight leg raise (SLR) test is a physical examination maneuver used to evaluate for lower back and leg pain. It is commonly used by doctors to diagnose or rule out conditions such as herniated disc, sciatica, and spinal stenosis.
During the SLR test, the patient lies flat on their back while the examiner lifts one of their legs straight up while keeping the knee extended. The test is considered positive if the patient experiences pain in their lower back, hip, or leg at an angle of between 30 and 70 degrees.
A positive test result may indicate nerve root irritation or compression, which can be caused by conditions such as a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or piriformis syndrome.
However, it is important to note that a positive SLR test alone is not sufficient to make a diagnosis and should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings and diagnostic tests.
It is important to perform the SLR test carefully and with caution, as it can exacerbate symptoms in patients with certain conditions, such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis. ONLY DONE BY DOCTORS OR Healthcare professional. Do not try this at home.
Investigations to rule out Sciatica:-
Some of these investigations include:
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination can help identify any neurological deficits, muscle weakness, or sensory changes in the lower back, buttock, and leg.
- X-rays: X-rays of the lumbar spine can help identify any abnormalities, such as degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, or spondylolisthesis, which may contribute to sciatica symptoms.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI scans are often used to visualize the spinal cord and nerve roots and identify any abnormalities that may be causing sciatica symptoms, such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis.
- Electromyography (EMG): An EMG test measures electrical activity in muscles and can help identify nerve damage or dysfunction in patients with sciatica.
- Nerve conduction studies: Nerve conduction studies measure the speed of nerve impulses and can help identify nerve damage or dysfunction in patients with sciatica.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate investigations for diagnosing sciatica and ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms.
there are different diagnostic workup are also done to understand the exact cause of sciatica. It includes different blood test for TB spine, osteoporosis, Vit B12 Deficiency, Vit D 3 Deficiency etc.
Treating Your Back Pain
The treatment for back pain depends on the underlying cause and severity of the pain. Here are some general guidelines for managing back pain:
- Rest: If the back pain is due to a strain or sprain, rest can help alleviate the pain. However, prolonged bed rest is generally not recommended as it can lead to muscle weakness and stiffness.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Heat and ice therapy: Applying heat or ice to the affected area can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Apply heat for 20-30 minutes at a time, and ice for 10-15 minutes at a time.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can provide exercises to help stretch and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, which can reduce pain and prevent future episodes.
- Chiropractic care: Chiropractic adjustments can help improve spinal alignment and relieve pressure on nerves, which can alleviate back pain. (Very popular outside India)
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct structural problems in the spine, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Medication : contact your doctor for pain relief drugs .
Physiotherapy for backache and Sciatica
Physiotherapy can be an effective treatment for back pain and sciatica. Here are some ways physiotherapy can help:
- Exercise therapy: A physiotherapist can design an exercise program tailored to your specific needs, which can help alleviate pain, improve flexibility, and strengthen the muscles supporting the spine.
- Manual therapy: Techniques such as massage, mobilization, and manipulation can help reduce pain and improve mobility in the affected area.
- Education: A physiotherapist can educate you about proper posture, body mechanics, and ergonomics, which can help prevent future episodes of back pain.
- Modalities: Modalities such as ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and heat or cold therapy can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Traction: Traction can help decompress the spine and reduce pressure on the affected nerve roots, which can alleviate pain and improve mobility.
- Functional training: A physiotherapist can help you learn how to perform daily activities with proper body mechanics, which can reduce the risk of future episodes of back pain.
Conclusion
Back pain and sciatica can be debilitating conditions that can impact your daily life. However, with the right treatment plan, it is possible to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and prevent future episodes.
Treatment options may include rest, pain relief, physical therapy, chiropractic care, or surgery, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the pain. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate treatment plan for your specific needs.
Additionally, incorporating healthy habits into your daily routine, such as maintaining proper posture, staying physically active, and managing stress, can help prevent future episodes of back pain and sciatica.
Please click here for such health updates