11 Best Plant-Based Proteins for a Healthy Diet
Best Plant-Based Proteins. In today’s health-conscious world, more people are embracing plant-based diets for their numerous benefits. Plant-based proteins offer a rich source of essential nutrients, support heart health, aid in weight management, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Whether you’re a vegetarian, vegan, or simply looking to incorporate more plant-based options into your meals, this article will guide you through the best plant-based proteins to enhance your diet.
Introduction
Plant-based proteins have gained popularity due to their positive impact on overall health and the environment. By replacing animal-based proteins with plant-based alternatives, individuals can enjoy a wide range of health benefits while reducing their carbon footprint.
Understanding Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins are derived from sources such as legumes, grains, nuts, seeds, and vegetables. Unlike animal proteins, which contain all essential amino acids, plant proteins may lack one or more of these amino acids. However, by combining various plant protein sources, individuals can ensure they receive all essential amino acids necessary for optimal nutrition.
Benefits of Plant-Based Proteins
Rich in Essential Nutrients
Plant-based proteins are not only a great source of protein but also provide a wide array of essential nutrients. They are rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which contribute to overall well-being and support various bodily functions.
Promote Heart Health
Plant-based proteins are generally low in saturated fat and cholesterol, making them heart-healthy choices. Consuming these proteins in place of animal proteins can help lower the risk of heart disease, hypertension, and high cholesterol levels.
Aid in Weight Management
Plant-based proteins are typically lower in calories and higher in fiber compared to animal proteins. The high fiber content helps promote satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating and aiding in weight management.
Reduce the Risk of Chronic Diseases
A diet rich in plant-based proteins has been associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and obesity. The abundance of antioxidants and phytochemicals in plant-based foods contributes to their disease-fighting properties.
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources

When it comes to plant-based proteins, there is a wide variety of options to choose from. Incorporating these protein sources into your diet can provide the necessary amino acids and other nutrients your body needs. Here are some of the best plant-based proteins to consider:
Lentils
Lentils are legumes packed with protein, fiber, and various essential nutrients. They are versatile and can be used in soups, stews, salads, and side dishes.
Chickpeas
Chickpeas, also known as garbanzo beans, are a staple in many cuisines. They are a great source of protein, fiber, and folate. Enjoy them in hummus, salads, curries, or roasted for a crunchy snack.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a complete protein source and a popular grain alternative. It contains all essential amino acids, making it an excellent choice for those following a plant-based diet. Use quinoa in salads, stir-fries, or as a side dish.
Hemp Seeds
Hemp seeds are a nutritional powerhouse, providing a good balance of protein, healthy fats, and essential fatty acids. Sprinkle them on top of yogurt, blend them into smoothies, or incorporate them into baked goods.
Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants. They can be used as a thickening agent in recipes, added to smoothies, or used to make delicious chia seed pudding.
Spirulina
Spirulina is a blue-green algae that offers a complete protein profile. It is also a great source of iron, vitamins, and minerals. Add spirulina powder to smoothies or use it in energy bars and snacks.
Tempeh
Tempeh is a fermented soy product with a nutty flavor and a firm texture. It is high in protein, probiotics, and other beneficial nutrients. Use tempeh in stir-fries, sandwiches, or as a meat substitute in various dishes.
Tofu
Tofu is made from soy milk and is an incredibly versatile ingredient. It is an excellent source of protein and contains all essential amino acids. Use tofu in stir-fries, curries, soups, or grilled as a meat alternative.
Edamame
Edamame are young soybeans that are harvested before they harden. They are rich in protein, fiber, and several vitamins and minerals. Enjoy them steamed, boiled, or added to salads and stir-fries.
Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds, provide a good amount of protein, healthy fats, and essential nutrients. Snack on them or sprinkle them over salads and cereals.
Nutritional Yeast
Nutritional yeast is a deactivated yeast that is popular for its cheesy flavor and nutritional content. It is a good source of protein, B vitamins, and minerals. Use nutritional yeast as a topping for popcorn, pasta, or roasted vegetables.
Incorporating Plant-Based Proteins into Your Diet
Adding plant-based proteins to your meals doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some simple and delicious ways to incorporate them into your diet:
Breakfast Ideas
- Start your day with a protein-packed smoothie made with plant-based protein powder, fruits, and greens.
- Enjoy a bowl of oatmeal topped with nuts, seeds, and a dollop of nut butter for added protein and healthy fats.
- Make a tofu scramble with vegetables and spices as a savory and protein-rich breakfast option.
Lunch and Dinner Options
- Prepare a colorful salad with a variety of vegetables, leafy greens, and your choice of plant-based proteins like chickpeas or quinoa.
- Cook a hearty lentil or bean soup loaded with vegetables for a filling and nutritious meal.
- Try a stir-fry with tofu or tempeh, paired with a mix of colorful vegetables and your favorite sauce.
Snack Suggestions
- Snack on roasted chickpeas or edamame for a crunchy and protein-packed treat.
- Prepare a batch of homemade energy balls using dates, nuts, and seeds for a convenient and nutritious snack.
- Enjoy a handful of trail mix with a combination of dried fruits, nuts, and seeds for a satisfying and protein-rich snack.
Protein Combinations for Optimal Nutrition
While individual plant-based proteins may not provide all essential amino acids, combining different protein sources can ensure you meet your nutritional needs. Here are some protein combinations to enhance your diet:
Combining Legumes with Whole Grains
Pairing legumes like lentils, chickpeas, or beans with whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, or whole wheat bread creates a complete protein source. This combination provides all essential amino acids necessary for proper nutrition.
Pairing Legumes with Nuts and Seeds
Combining legumes with nuts and seeds also creates a complementary protein source. For example, you can mix hummus (made from chickpeas) with sesame tahini (made from sesame seeds) for a nutritious and delicious protein-rich snack.
Enhancing Protein Absorption with Vitamin C
Consuming plant-based proteins along with vitamin C-rich foods can enhance protein absorption. For instance, pair a lentil salad with citrus fruits or add bell peppers to your tofu stir-fry to maximize nutrient uptake.
Meeting Protein Needs on a Plant-Based Diet
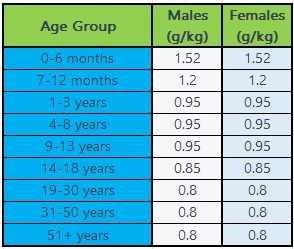
It’s important to ensure you meet your protein needs when following a plant-based diet. The Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) for protein is around 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. However, certain individuals, such as athletes and active individuals, may require slightly more protein.
Recommended Daily Intake
To determine your protein requirements, multiply your weight in kilograms by 0.8 grams. For example, if you weigh 68 kilograms, you would need approximately 54 grams of protein per day.
Protein Requirements for Athletes and Active Individuals
Athletes and those who engage in regular intense physical activity may require higher protein intake to support muscle recovery and growth. Consult a registered dietitian or sports nutritionist to determine your specific protein needs based on your activity level and training goals.
Plant-Based Protein Supplements
In some cases, incorporating plant-based protein supplements can help meet your protein requirements. There are various options available, including pea protein, rice protein, and hemp protein powders. Choose high-quality, minimally processed supplements and consult with a healthcare professional or dietitian before adding them to your routine.
Overcoming Concerns and Misconceptions
There are common concerns and misconceptions surrounding plant-based proteins. However, understanding the facts can help alleviate any worries you may have:
Complete Proteins from Plant Sources
While individual plant-based proteins may not be complete on their own, combining different protein sources throughout the day ensures you receive all essential amino acids.
Digestibility of Plant Proteins
Plant-based proteins can be easily digested and absorbed by the body. Consuming a varied and balanced plant-based diet ensures you receive all the necessary amino acids and nutrients.
Iron and Calcium Considerations
Plant-based sources of iron, such as lentils, tofu, and spinach, can provide adequate iron intake. Pairing iron-rich foods with vitamin C sources enhances iron absorption. Similarly, plant-based sources of calcium, such as tofu, fortified plant milks, and leafy greens, can support bone health when consumed as part of a well-rounded diet.
Plant-Based Proteins for Specific Dietary Needs
Plant-based proteins offer options for individuals with specific dietary needs:
Gluten-Free Options
For those following a gluten-free diet, plant-based protein sources like lentils, quinoa, chickpeas, and nuts are naturally gluten-free and can be enjoyed without concerns.
Vegan and Vegetarian Choices
Plant-based proteins are the cornerstone of vegan and vegetarian diets, providing ample options for protein intake without the need for animal products.
Allergen-Friendly Alternatives
Plant-based proteins can be suitable alternatives for individuals with common food allergies or intolerances, such as soy, dairy, or egg allergies. Options like lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, and seeds can provide protein without triggering allergic reactions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Opting for plant-based proteins also promotes sustainability and reduces the environmental impact of food production:
Reduced Carbon Footprint
Plant-based proteins generally have a lower carbon footprint compared to animal proteins. By choosing plant-based options, you contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
Conservation of Water Resources
Producing plant-based proteins requires significantly less water compared to animal-based proteins. By embracing plant-based alternatives, you help conserve valuable water resources.
Preservation of Biodiversity
Plant-based diets promote biodiversity by reducing the demand for intensive animal agriculture, which often leads to deforestation and habitat destruction. Choosing plant-based proteins contributes to preserving ecosystems and protecting wildlife.
Conclusion
Incorporating plant-based proteins into your diet is a fantastic way to improve your health, support the environment, and enjoy a wide variety of delicious and nutritious foods. With options like lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, tofu, and more, there is an abundance of plant-based proteins to suit every palate and dietary preference. Start incorporating these protein-rich options into your meals and experience the benefits of a plant-powered lifestyle.
FAQs
- Can plant-based proteins provide all essential amino acids?
- Yes, by combining different plant-based protein sources throughout the day, you can obtain all essential amino acids necessary for optimal nutrition.
- Are plant-based proteins suitable for muscle building?
- Yes, plant-based proteins can support muscle building when consumed in adequate amounts and combined with regular exercise.
- How can I make sure I’m getting enough protein on a plant-based diet?
- By including a variety of plant-based protein sources such as legumes, grains, nuts, seeds, and soy products in your meals, you can meet your protein needs.
- Can plant-based proteins support weight loss?
- Yes, plant-based proteins are typically lower in calories and higher in fiber, which can aid in weight management and promote feelings of fullness.
- Are plant-based proteins more sustainable than animal-based proteins?
- Yes, plant-based proteins have a lower carbon footprint and require less water and resources compared to animal-based proteins.