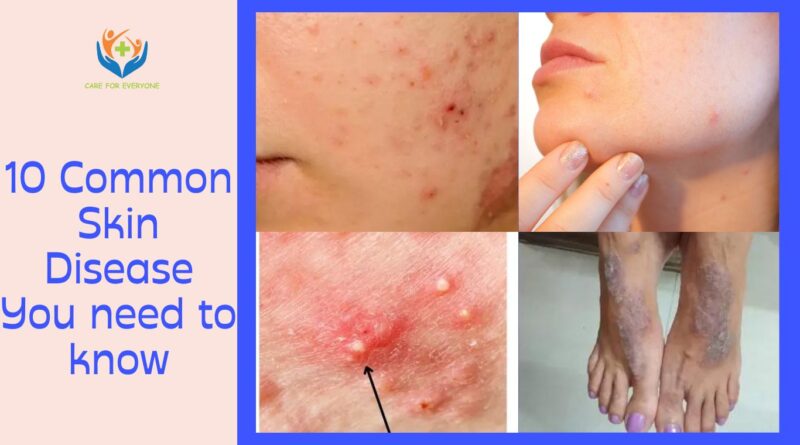
10 Common Skin Disease You need to know
Introduction
Your skin is the largest organ of your body and it serves as a barrier to protect you from external factors like pollution, bacteria, and viruses. However, skin diseases can cause a lot of discomforts, and some can even be life-threatening. In this article, we will be discussing five common skin diseases that you need to know.
1. Acne (Acne vulgaris)

Acne vulgaris, commonly known as acne, is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads on the face, chest, and back. Acne is most common during adolescence, but it can affect people of all ages.
Cause:
Acne is caused by a combination of factors, including hormonal changes, genetics, and bacteria. When the hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, it creates an environment where bacteria can thrive, leading to inflammation and the formation of pimples.
Types:
There are different types of acne, including:
- Whiteheads: Small, white bumps on the skin that are caused by clogged pores.
- Blackheads: Small, dark bumps on the skin that are caused by clogged pores and oxidation of the trapped sebum.
- Papules: Small, red bumps that are tender to the touch.
- Pustules: Red, inflamed bumps with a white or yellow center.
- Cysts: Large, painful bumps that contain pus.
Probable treatment:
Treatment options for acne depend on the severity of the condition. Mild to moderate acne can often be treated with over-the-counter creams and gels that contain benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid. These medications work by reducing inflammation and killing bacteria.
In more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics to help control the bacteria causing the acne. In addition, retinoids, which are derived from vitamin A, can help unclog pores and reduce inflammation. For women with hormonal acne, birth control pills or spironolactone may be recommended.
It is important to note that some acne treatments can cause side effects, such as dryness, redness, and peeling. It is essential to follow the instructions of a dermatologist or healthcare provider when using these medications.
Conclusion:
Acne is a common skin condition that can cause a lot of discomfort and affect a person’s self-esteem. While it is most common during adolescence, acne can affect people of all ages. Understanding the cause and different types of acne can help individuals seek appropriate treatment. With proper care and treatment, most cases of acne can be effectively managed.
2. Atopic dermatitis (Eczema)
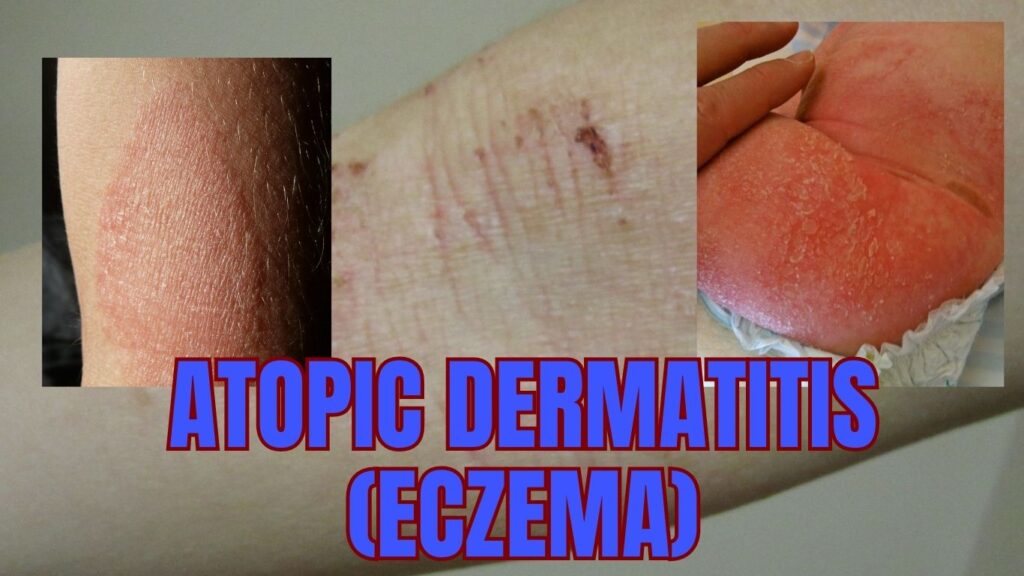
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It is a common condition, affecting approximately 10-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide. Eczema can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life, but with proper management, symptoms can be controlled.
Cause:
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetics, immune dysfunction, and environmental factors. Individuals with eczema have a weakened skin barrier, which allows irritants and allergens to penetrate the skin and trigger inflammation. Factors that can worsen eczema symptoms include stress, dry air, harsh soaps or detergents, and certain foods.
Types:
There are several types of eczema, including:
- Atopic dermatitis: This is the most common type of eczema, often occurring in individuals with a personal or family history of allergies or asthma.
- Contact dermatitis: This type of eczema occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen, such as certain fabrics or chemicals.
- Nummular dermatitis: This type of eczema causes coin-shaped patches of irritated skin, often on the arms and legs.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: This type of eczema causes greasy, yellowish scales on the scalp and face.
Probable treatment:
Treatment for eczema focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Moisturizing the skin regularly with an emollient or cream can help improve the skin’s barrier function and prevent dryness. Topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors can be used to reduce inflammation and itchiness.
In some cases, oral antihistamines may be recommended to alleviate itching. For severe cases, phototherapy or oral immunosuppressants may be prescribed. It is also important to avoid triggers that can exacerbate symptoms, such as harsh soaps or detergents, and certain foods.
Conclusion:
Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, is a chronic skin condition that can cause discomfort and disrupt daily life. While the exact cause is unknown, eczema is believed to be a combination of genetics, immune dysfunction, and environmental factors. Understanding the different types of eczema and appropriate treatment options can help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
3. Shingles (Herpes Zoster)
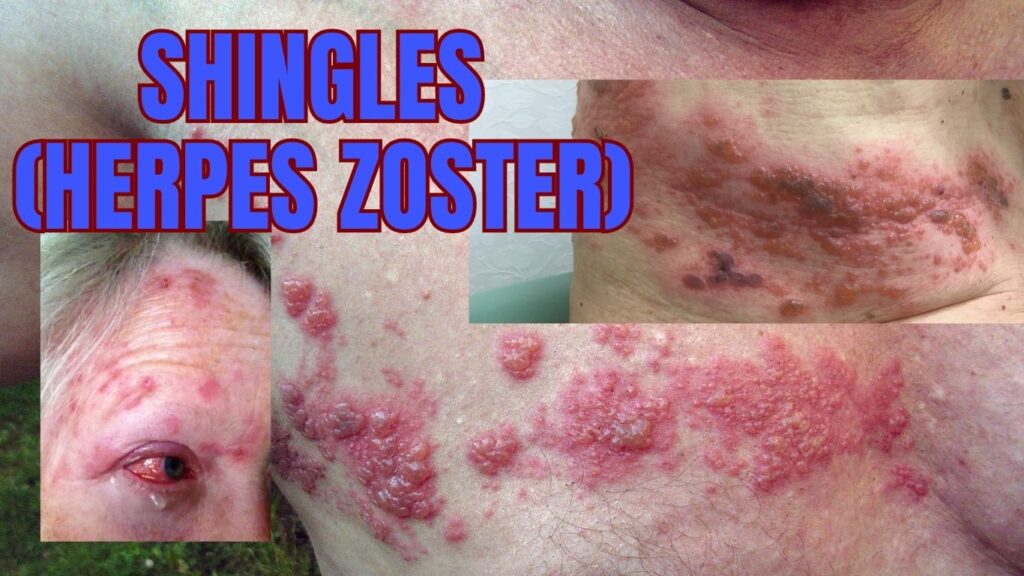
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash. The condition is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains in the body and can reactivate years later, causing shingles.
Cause:
Shingles is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, which remains dormant in the nerve cells of the body after a person recovers from chickenpox. The virus can reactivate due to a weakened immune system, stress, or aging. Shingles is not contagious, but a person with shingles can spread the virus to someone who has not had chickenpox or been vaccinated against it.
Types:
There is only one type of shingles, but it can manifest in different ways. The most common form of shingles is a painful, blistering rash that appears on one side of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, headache, and sensitivity to light.
Probable treatment:
Treatment for shingles involves antiviral medications, such as acyclovir or valacyclovir, to reduce the severity and duration of the rash and other symptoms. Pain medications and topical creams may also be recommended to alleviate pain and itching.
In addition to medication, it is important to rest and avoid stress as much as possible. Keeping the rash clean and covered can help prevent the spread of the virus and reduce the risk of infection. Individuals with shingles should also avoid contact with individuals who have not had chickenpox or been vaccinated against it.
Prevention:
The best way to prevent shingles is through vaccination. The shingles vaccine, also known as the herpes zoster vaccine, is recommended for adults over the age of 50. The vaccine can reduce the risk of developing shingles and reduce the severity of symptoms if the virus does reactivate.
Conclusion:
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is a viral infection that can cause a painful rash and other symptoms. It is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, which remains dormant in the body after a person recovers from chickenpox. Treatment for shingles involves antiviral medications, pain relief, and rest. Prevention through vaccination is the best way to reduce the risk of developing shingles.
4. Hives (Urticaria)

Hives, also known as urticaria, is a skin condition characterized by itchy, raised welts on the skin. The welts can vary in size and shape and may be red or flesh-colored. Hives can appear suddenly and disappear quickly or persist for several days.
Cause:
Hives are caused by an immune system response that triggers the release of histamine and other chemicals in the skin. This can occur due to a variety of factors, including allergies to food, medications, or environmental triggers like pollen or pet dander. Other causes of hives include stress, infection, and exposure to cold or heat.
Types:
There are two types of hives: acute and chronic. Acute hives are short-lived and typically last less than six weeks. Chronic hives persist for longer than six weeks and can be more difficult to treat.
Probable treatment:
Treatment for hives involves identifying and avoiding the triggers that cause the condition. Antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine or loratadine, can also help reduce itching and inflammation. In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe corticosteroid medications or immunosuppressants to manage symptoms.
Prevention:
Preventing hives involves avoiding triggers and identifying any underlying health conditions that may be contributing to the condition. Keeping a diary of symptoms and triggers can help identify patterns and guide treatment. It may also be helpful to avoid exposure to known triggers and maintain good hygiene practices to prevent infections.
Conclusion:
Hives, or urticaria, is a skin condition characterized by itchy, raised welts on the skin. The condition is caused by an immune system response to various triggers, including allergies, stress, and temperature changes. Treatment involves avoiding triggers and managing symptoms with medications like antihistamines or corticosteroids. Preventing hives involves identifying triggers and maintaining good hygiene practices.
5. Sunburn

Sunburn is a type of skin damage that occurs when the skin is exposed to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays for an extended period of time. The condition can range from mild redness and irritation to painful blisters and peeling skin.
Cause:
Sunburn is caused by exposure to UV rays, which can damage the DNA in skin cells and lead to inflammation and skin damage. UV rays can come from natural sunlight or artificial sources like tanning beds. People with fair skin, light hair, and blue or green eyes are more susceptible to sunburn.
Types:
Sunburn can vary in severity, with mild cases causing redness and tenderness, while severe cases can cause blisters, fever, and chills. Long-term exposure to UV rays can also increase the risk of skin cancer.
Probable treatment:
Treatment for sunburn typically involves relieving the symptoms and preventing further damage. Applying cool compresses or taking a cool bath can help reduce inflammation and pain. Moisturizing lotions or aloe vera gel can also soothe the skin and promote healing. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help with pain and inflammation.
In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe corticosteroid creams or oral medications to reduce inflammation and discomfort. It is important to stay hydrated and avoid further sun exposure until the skin has fully healed.
Prevention:
The best way to prevent sunburn is to avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours when the sun is strongest. Wearing protective clothing like hats, long sleeves, and sunglasses can also help reduce exposure. Using sunscreen with a high SPF and reapplying every two hours can also protect the skin from UV damage.
Conclusion:
Sunburn is a common skin condition that can cause redness, irritation, and pain. It is caused by exposure to UV rays from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. Treatment involves relieving symptoms and preventing further damage, while prevention involves avoiding sun exposure and using protective clothing and sunscreen.
6. Contact Dermatitis
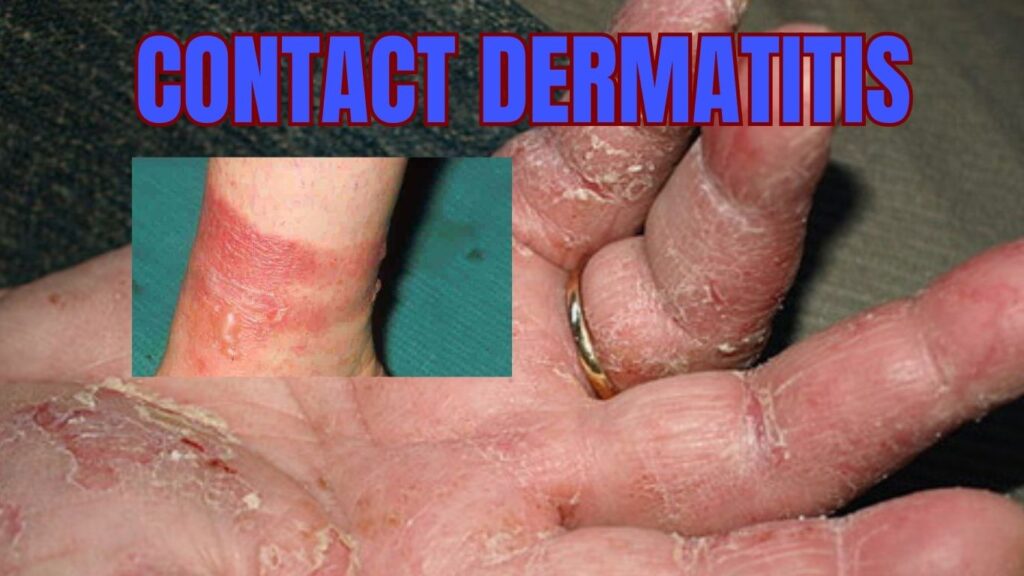
Contact dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen. The condition can cause redness, itching, and a rash, and can be acute or chronic.
Cause:
Contact dermatitis is caused by an immune system reaction to a substance that comes into contact with the skin. This can include irritants like soaps, detergents, and cleaning products, as well as allergens like cosmetics, plants, and metals like nickel. Some people may be more susceptible to contact dermatitis due to genetic factors or underlying health conditions.
Types:
There are two types of contact dermatitis: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis occurs when the skin is exposed to a substance that directly damages the skin, while allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the immune system overreacts to an allergen.
Probable treatment:
Treatment for contact dermatitis involves avoiding the irritant or allergen that caused the reaction. Topical corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and itching, while antihistamines may also be prescribed to relieve symptoms. In severe cases, a doctor may recommend light therapy or oral medications to manage symptoms.
Prevention:
Preventing contact dermatitis involves identifying and avoiding triggers. This may involve using protective clothing or gloves when handling irritants, avoiding known allergens, and practicing good hygiene to prevent infections. It is also important to maintain healthy skin by keeping it clean and moisturized.
Conclusion:
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition characterized by redness, itching, and a rash. The condition is caused by exposure to irritants or allergens, and treatment involves avoiding triggers and managing symptoms with topical or oral medications. Preventing contact dermatitis involves identifying triggers and practicing good hygiene and skin care.
7. Diaper Rash

Diaper rash is a common skin condition that affects infants and toddlers. It is characterized by redness and irritation in the diaper area and can be caused by a variety of factors.
Cause:
Diaper rash is most commonly caused by prolonged exposure to moisture, which can irritate the skin and cause inflammation. Other causes of diaper rash include friction from rubbing against the diaper, allergic reactions to materials in the diaper, and infections like yeast or bacteria.
Types:
There are several types of diaper rash, including:
- Irritant diaper rash: caused by prolonged exposure to urine or feces
- Allergic diaper rash: caused by an allergic reaction to materials in the diaper or wipes
- Candida diaper rash: caused by a yeast infection
- Bacterial diaper rash: caused by a bacterial infection
Probable treatment:
Treatment for diaper rash involves keeping the diaper area clean and dry, and using products like diaper rash creams or ointments to soothe the skin. In cases of bacterial or yeast infections, a doctor may prescribe antifungal or antibiotic medications.
Prevention:
Preventing diaper rash involves changing diapers frequently and keeping the diaper area clean and dry. Using a barrier cream or ointment can also help protect the skin from irritation. Avoiding harsh soaps and fragrances can also reduce the risk of diaper rash.
Conclusion:
Diaper rash is a common skin condition that affects infants and toddlers. It is caused by prolonged exposure to moisture, friction, allergic reactions, or infections. Treatment involves keeping the diaper area clean and dry and using creams or ointments to soothe the skin. Preventing diaper rash involves frequent diaper changes, good hygiene practices, and avoiding harsh products.
8. Rosacea

Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, inflammation, and sometimes acne-like bumps on the face. It typically affects people over the age of 30 and is more common in fair-skinned individuals.
Cause:
The exact cause of rosacea is unknown, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some triggers that can exacerbate symptoms include exposure to sunlight, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress.
Types:
There are four subtypes of rosacea:
- Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea: characterized by persistent redness and visible blood vessels
- Papulopustular rosacea: characterized by acne-like bumps and pus-filled lesions
- Phymatous rosacea: characterized by thickening of the skin and enlargement of the nose or other facial features
- Ocular rosacea: characterized by redness, itching, and burning of the eyes
Probable treatment:
Treatment for rosacea involves managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. This may involve using topical or oral medications to reduce inflammation and redness, as well as avoiding triggers and practicing good skin care habits. In severe cases, laser or light therapy may be recommended to reduce redness and visible blood vessels.
Prevention:
Preventing rosacea involves identifying triggers and avoiding them when possible. This may involve wearing sunscreen and protective clothing when outdoors, avoiding spicy or hot foods, and managing stress levels. Practicing good skin care habits, such as using gentle cleansers and moisturizers, can also help reduce symptoms.
Conclusion:
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, inflammation, and acne-like bumps on the face. It is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and treatment involves managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. Preventing rosacea involves avoiding triggers and practicing good skin care habits.
9. Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis)
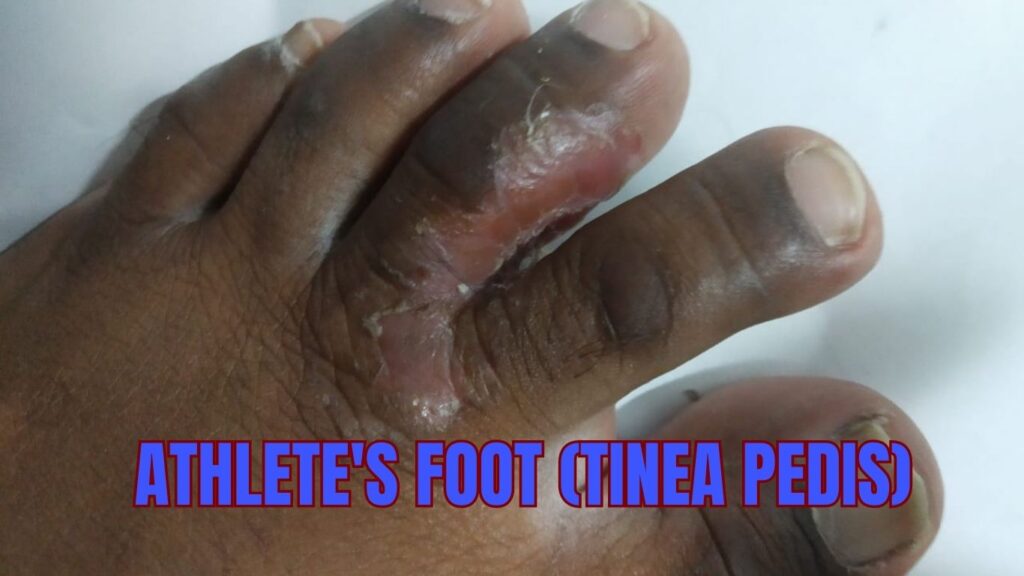
Athlete’s foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a fungal infection of the skin on the feet. It is a common condition, particularly among athletes and people who wear tight-fitting shoes or damp socks for extended periods.
Cause:
Athlete’s foot is caused by a group of fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the feet a prime location for infection. The infection can be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or by direct contact with an infected person.
Types:
There are several types of athlete’s foot, including:
- Interdigital: affects the skin between the toes
- Moccasin: affects the sole and sides of the foot
- Vesicular: causes fluid-filled blisters on the feet
- Ulcerative: causes open sores on the feet
Probable treatment:
Treatment for athlete’s foot typically involves topical antifungal medications, such as creams, ointments, or powders. In some cases, oral antifungal medications may be necessary to treat severe or persistent infections. Keeping the feet clean and dry and wearing breathable, moisture-wicking socks can also help prevent and treat athlete’s foot.
Prevention:
Preventing athlete’s foot involves taking steps to keep the feet clean and dry. This includes wearing breathable shoes and socks, changing socks regularly, and avoiding walking barefoot in public areas. It is also important to avoid sharing shoes, socks, or other personal items with others to reduce the risk of infection.
Conclusion:
Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection of the skin on the feet that is caused by dermatophytes. It can be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or direct contact with an infected person. Treatment typically involves topical or oral antifungal medications, as well as good foot hygiene practices. Preventing athlete’s foot involves keeping the feet clean and dry and avoiding sharing personal items with others.
10. Basal Cell Carcinoma
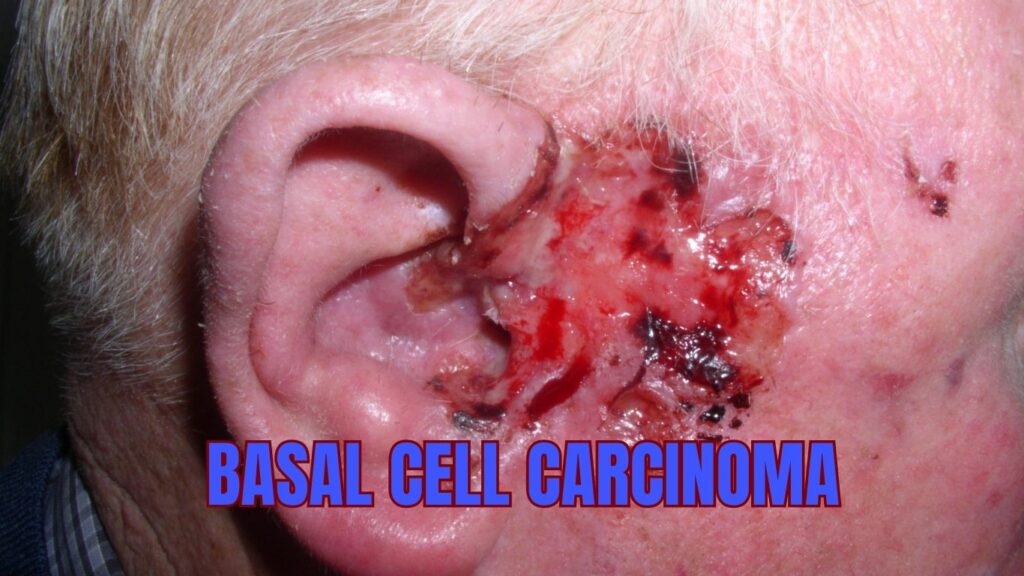
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a type of skin cancer that arises from basal cells, which are located in the deepest layer of the epidermis. It is the most common form of skin cancer and typically develops on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun.
Cause:
The main cause of basal cell carcinoma is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. People with fair skin, light-colored hair, and blue or green eyes are at higher risk for developing BCC. Other risk factors include a family history of skin cancer, exposure to certain chemicals, and a weakened immune system.
Types:
There are several subtypes of basal cell carcinoma, including:
- Nodular BCC: characterized by a shiny, pearly bump on the skin
- Superficial BCC: characterized by a scaly, red patch on the skin
- Pigmented BCC: characterized by a brown or black lesion on the skin
- Morpheaform BCC: characterized by a white, waxy scar-like lesion on the skin
Probable treatment:
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma typically involves surgical removal of the cancerous lesion. This may involve a simple excision, Mohs surgery, or curettage and electrodessication. In some cases, topical medications or radiation therapy may be used to treat BCC. The specific treatment approach will depend on the size and location of the lesion, as well as the individual’s overall health.
Prevention:
Preventing basal cell carcinoma involves reducing exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds. This may involve wearing protective clothing, such as hats and long-sleeved shirts, and using sunscreen with a high SPF. It is also important to avoid tanning beds and to seek shade during peak sun hours. Regular skin exams and self-exams can help detect BCC early and improve outcomes.
Conclusion:
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that arises from basal cells in the skin. It is typically caused by exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Treatment involves surgical removal of the lesion, and prevention involves reducing exposure to UV radiation through protective measures such as wearing sunscreen and avoiding tanning beds. Regular skin exams can help detect BCC early and improve outcomes.
What are the most common skin disease?
ACNE -Acne vulgaris, commonly known as acne, is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads on the face, chest, and back. Acne is most common during adolescence, but it can affect people of all ages.
What are 5 common skin diseases?
Acne (Acne vulgaris),Atopic dermatitis (Eczema),Shingles (Herpes Zoster),Hives (Urticaria) & Sunburn
Which is a serious skin disease?
SKIN CANCER – LIKE Basal Cell Carcinoma & Psoriasis are serious skin diseases.
PLEASE DON’T DO SELF TREATMENT . ALWAYS CONSULT YOUR DOCTOR OR DERMATOLOGIST IN THIS CASE.
Please read Health Update here
Please comment on the article and let us know What else you want to know about your health. We will be happy to help.